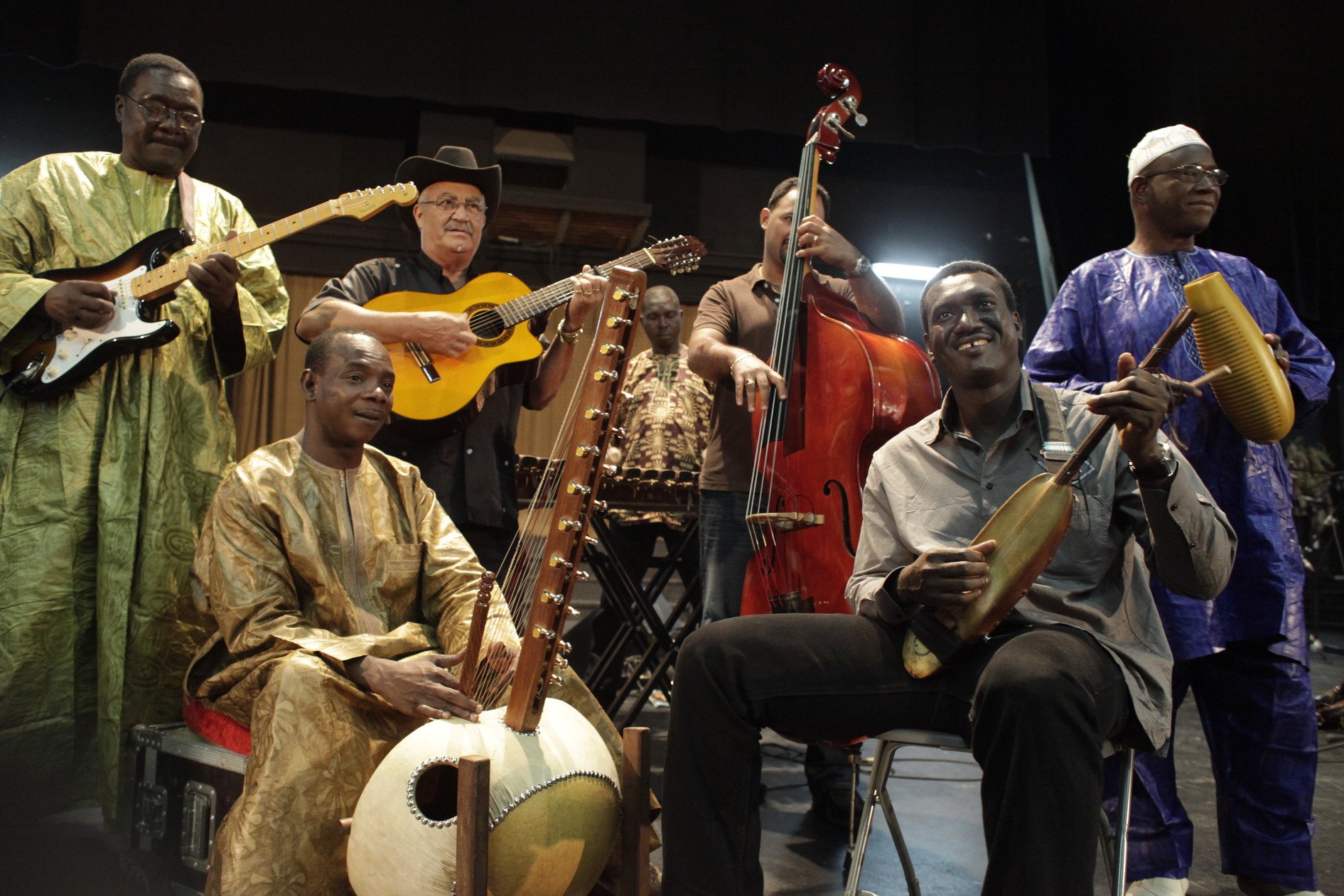
"Traditional African music is symbolic, an expression and validation of psychic energy."
W. Komla Amoakua
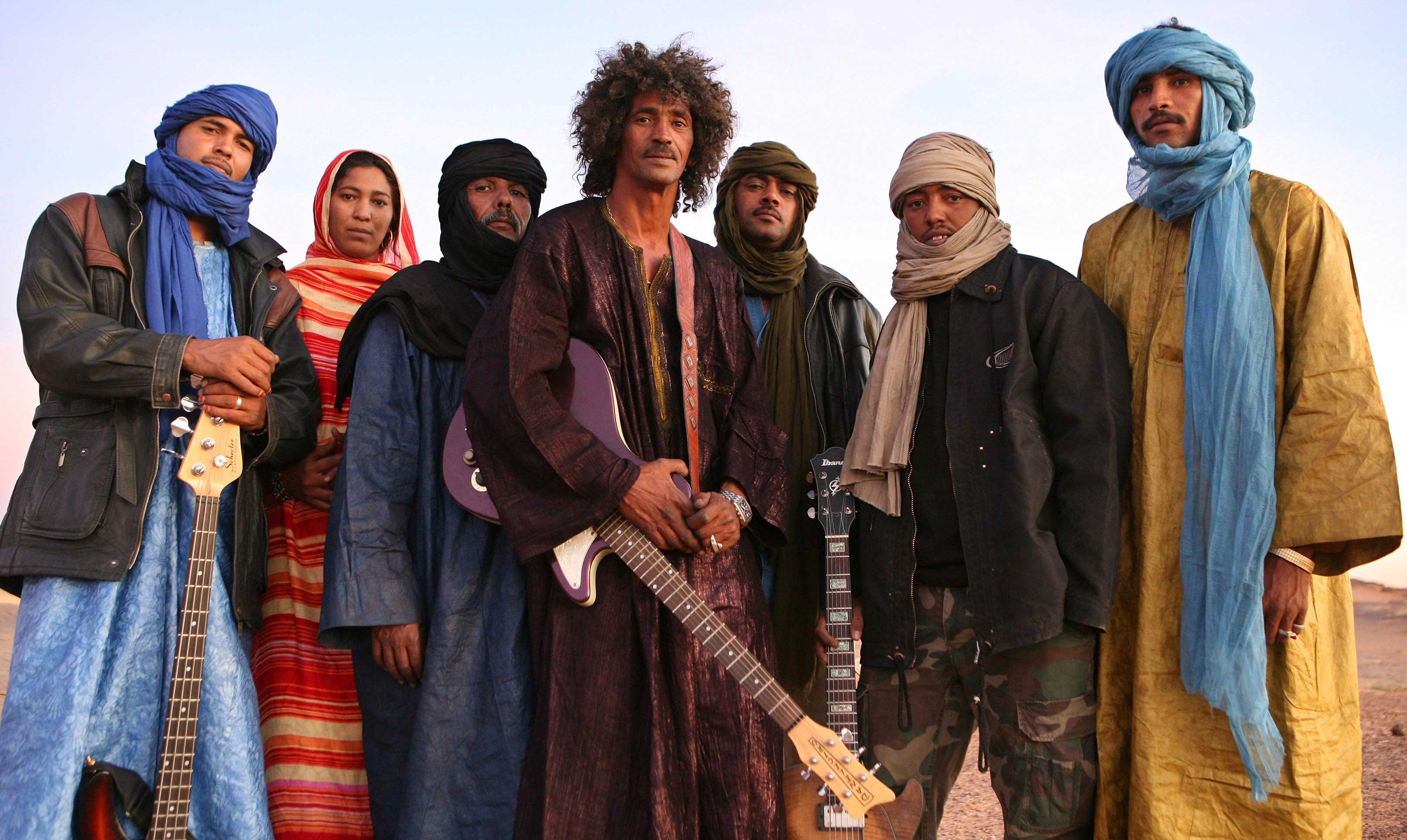
In traditional Africa, music is an integral part of life and is linked with the worldview of the society in which it is produced. It has social, ritual, and ceremonial functions as well as some purely recreational purposes. Traditional art forms, including music, are rooted in mythology, legends, and folklore, and are associated with gods, ancestors and heroes. Musical activities are ritualized and intended to link the visible world with the invisible. Dancing is often an important part of the ritual and spiritual aspect of music.
Percussion instruments are the most popular instrument in African societies. Rattles, friction sticks, bells, clappers, and cymbals are popular. Many groups also use the sansa and xylophones. Numerous types of drums are also used. Various wind instruments are made out of tusks, horns, conch shells, wood or gourds. Styles of vocal music vary from area to area. This is due partly to the different languages spoken in different areas. Most African languages are tonal languages which are reflected in the singing.
Traditional African music does not have a written tradition. This makes it difficult to notate the music using the Western staff. The pitches and subtle differences in intonation do not translate easily. The Western scale patterns that relate most closely to African music are tetratonic, pentatonic, hexatonic or heptatonic arrangements. Melodic patterns are affected by intonation patterns of the language.
The rhythmic aspect of African music unites the music of various groups and areas. Rhythm is made of patterns; similar patterns are found throughout all of Africa. Harmonization is typically created through singing in thirds, fourths and fifths, parallel to the main melody.
While drumming is very popular in Africa and is more important than melodic music in some societies, melodic music is important in others. The mbira is one of the most popular melodic instruments in Africa. Different cultures use the mbira in different ways. Also, the mbira exists in different forms in different cultures. Some mbira are used for entertainment and others for religious ceremonies. Often, the people who can own and play the mbira are restricted to chiefs or other important people, especially when it is being played for religious purposes. .